When it comes to your business, at some point or another you may need to borrow money from investors, lenders, etc. to help grow. One thing they typically look at before shelling out any funds is your financial metrics, like leverage ratios. This article breaks down:
- Leverage ratio definition
- 5 leverage ratios to keep in mind
- What is considered a good ratio
What is a leverage ratio?
Leverage looks at the ratio of a company’s debt to the value of its equity. A leverage ratio measures your company financially and tells you:
- How much capital is from debt
- Your ability to meet financial obligations
Basically, leverage ratios can show you the proportion of debt compared to equity or capital. To find your ratio, you can compare debt to your accounts using your income statement, balance sheet, or cash flow statement.
Your ratio can give you an indication of how your business finances assets and operations. It can also tell accountants, analysts, investors, lenders, and finance managers how your business is using leverage. A leverage calculation can also help you:
- Evaluate whether you can pay off debts as they’re due
- Control your debts
- Determine how changes will impact income
- Make smart financial decisions
Types of leverage in business
There are a few types of leverage in business, including:
- Financial
- Operating
- Combined
Financial
A financial leverage ratio looks at how much debt your company uses or will be using to finance business operations.
Operating
An operating leverage ratio compares fixed costs to variable costs. A company with a higher operating leverage ratio has a high ratio of fixed costs to revenue.
Combined
A combined leverage ratio looks at both operating and financial leverage. For example, operating income influences the upper half of the income statement while financial leverage impacts the bottom half.
Common types of leverage ratios
There are a variety of financial leverage ratio formulas you can use to determine how your business is doing financially. These include:
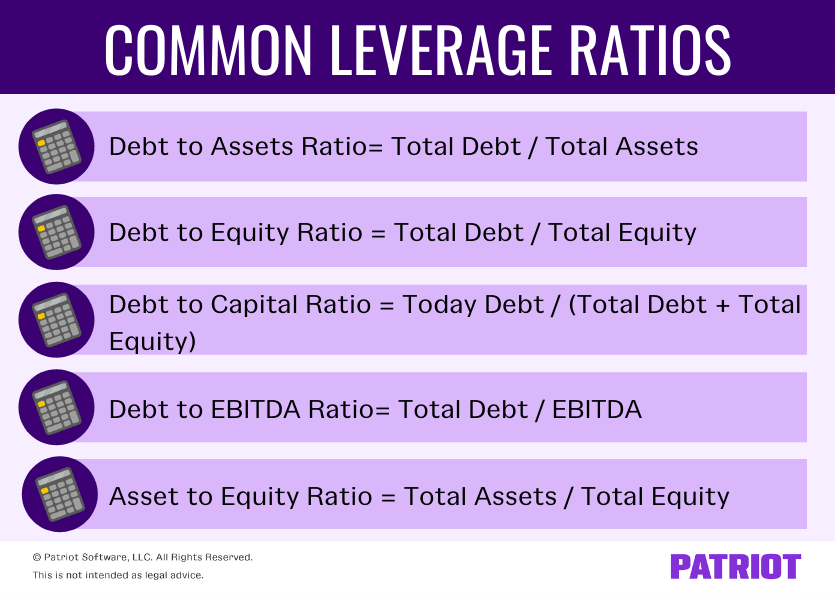
- Debt to assets ratio= Total Debt / Total Assets
- Debt to equity ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
- Debt to capital ratio = Today Debt / (Total Debt + Total Equity)
- Debt to EBITDA ratio= Total Debt / Earnings Before Interest Taxes Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA)
- Asset to equity ratio = Total Assets / Total Equity
As you can see, the ratios look at debt compared to another metric or vice versa. You can use these ratios to determine your proportion of debt and make financial decisions.
What is a good leverage ratio?
A healthy leverage ratio can vary depending on your business and the industry you’re in. It can also depend on which ratio you’re computing.
When it comes to debt to assets, you ideally want a ratio of 0.5 or less. A ratio less than 0.5 shows that no more than half of your company is financed by debt. A higher ratio (e.g., 0.8) may indicate that a business has incurred too much debt. But again, a higher ratio may be more acceptable in certain industries (e.g., capital-intensive businesses).
Do research to find out healthy ratios for your industry. If you have questions or concerns about your business’s ratios, consider consulting an accountant or another professional.
Leverage ratio examples
Check out a few examples below to see how to calculate leverage ratios. Then, use your company’s totals to do a leverage ratio calculation of your own.
Example 1
Say your business has $30,000 in assets, $12,000 in debt, and $20,000 in equity. Use these totals to find multiple leverage ratios for your business:
- Debt to equity = Debt / Equity
- $12,000 / $20,000 = 0.60
- Debt to assets = Debt / Assets
- $12,000 / $30,000 = 0.40
- Debt to capital = Debt / Capital
- $12,000 / ($12,000 + $20,000) = 0.375
Your debt to equity ratio (0.60) shows that your equity makes up most of your business’s resources.
Example 2
Now let’s say your business has the following financial information:
- $100,000 in assets
- $35,000 of debt
- $50,000 in equity
- $5,000 in EBITDA
Use your total to calculate your ratios for the period:
- Debt to assets ratio= Total Debt / Total Assets
- $35,000 / $100,000 = 0.35
- Debt to equity ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
- $35,000 / $50,000 = 0.70
- Debt to capital ratio = Total Debt / (Total Debt + Total Equity)
- $35,000 / ($35,000 + $50,000) = 0.412
- Debt to EBITDA ratio= Total Debt / EBITDA
- $35,000 / $5,000 = 7.0
- Asset to equity ratio = Total Assets / Total Equity
- $100,000 / $50,000 = 2.0
Your debt to equity ratio shows that your business uses less than half of its resources (0.35) for debts, like loans and other liabilities.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.